Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS) provides a managed SQL database engine without having to worry about infrastructure management. In this post, we will walk through the steps to set up a SQL Server database on RDS.
Prerequisites
To get started, you will need:
- An AWS account
- Basic understanding of SQL Server and databases
- A VPC and subnet created to deploy the RDS instance
Creating the RDS Instance
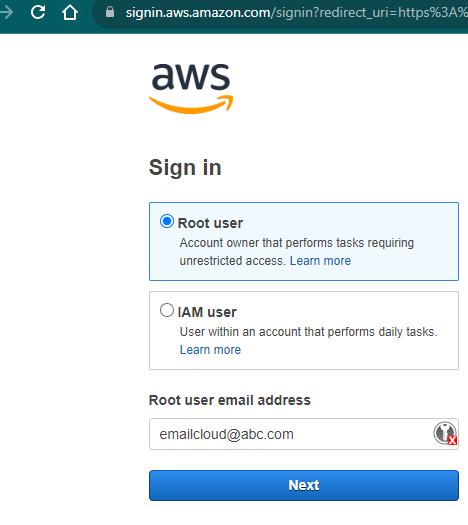
Step 1: Sign in to AWS Console
Open your web browser and go to the AWS Management Console (https://aws.amazon.com/console/).
Sign in with your AWS credentials.
Step 2: Navigate to RDS Dashboard and Engine Options
In the AWS Management Console, search for “RDS” in the search bar or find it in the Services dropdown. Select the engine type. In this case, choose “Microsoft SQL Server”.Choose the edition and version you want to use.

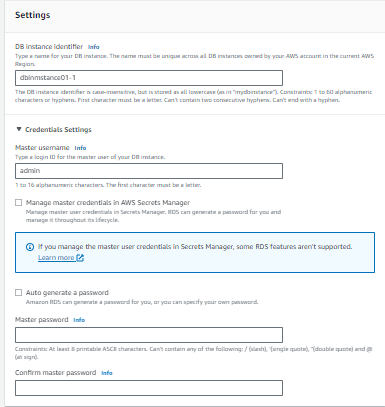
Step 3: Specify DB Details and Setting
DB Instance Identifier: Provide a unique identifier for your DB instance.
Master Username and Password: Set a username and password for your master user.
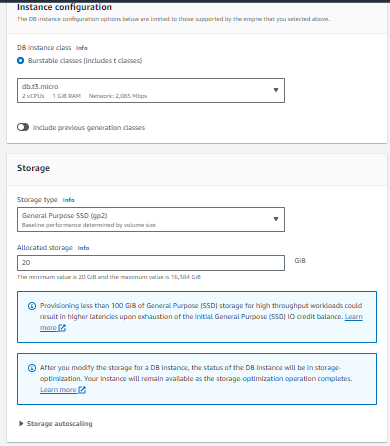
Step 4: Instance Configuration and Storage
DB Instance Class: Choose the appropriate instance type based on your requirements and budget.
Multi-AZ Deployment: Select if you want a high availability setup with a standby instance in a different Availability Zone.
Storage Type: Select the type of storage (e.g., General Purpose SSD, Provisioned IOPS).
Allocated Storage: Specify the amount of storage in GB.
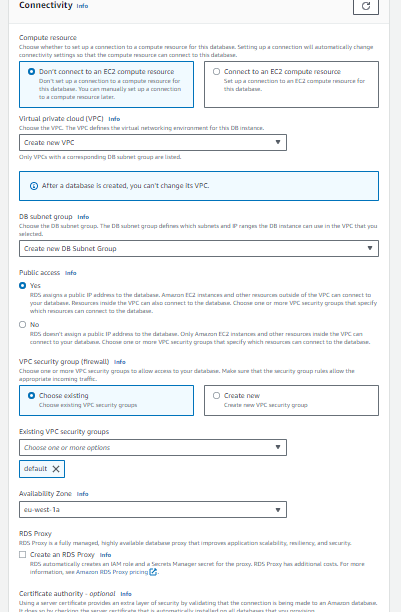
Step 5: Configure Advanced Settings and Connectivity
VPC and Subnet Settings: Choose the Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) and Subnets for your RDS instance.
Public Accessibility: Decide whether the DB instance should be publicly accessible or not.
Availability Zone: You can either choose to let AWS automatically select an Availability Zone or select one manually.
Database Options: Configure the necessary options such as port, parameter group, and option group.
Step 6: Database Authentication
Choose the preferred method for authentication. You can select either password authentication or IAM authentication.
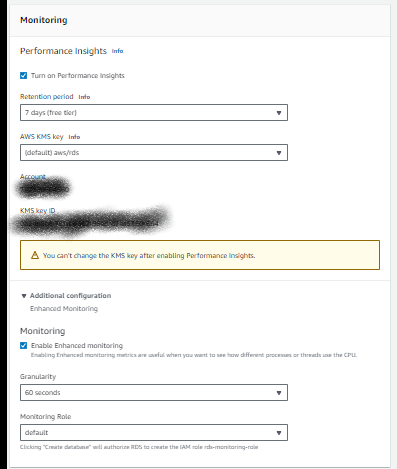
Step 7: Monitoring
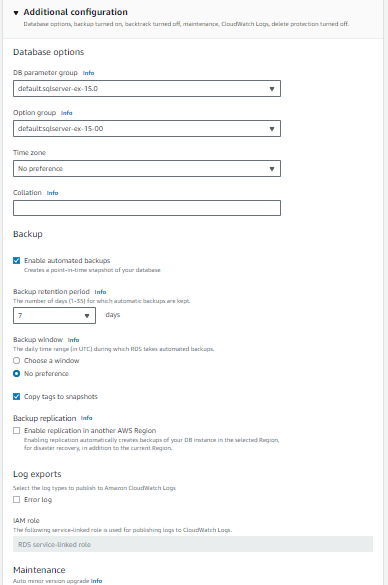
Step 8: Additional Configuration and Backup and Maintenance
Database Name: Specify the name of your initial database.
Option Group: Choose or create an option group for your database. This helps in managing options and settings.
Set up your preferred backup and maintenance settings, including the backup retention period.
Step 9: Monitoring and Maintenance
Choose if you want to enable Enhanced Monitoring or not.
Set up the maintenance window for your RDS instance.
Step 10: Tags (Optional)
Add any tags that you want to help organize and identify your resources.
Step 11: Review and Create
Review all the configurations you’ve made.
If everything looks correct, click “Create Database”.
Step 12: Wait for Database Creation
The database creation process may take a few minutes to an hour depending on the selected options and database size.
Monitor the progress in the RDS dashboard.
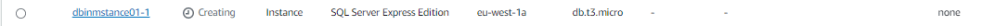
Step 13: Accessing Your SQL Server Instance
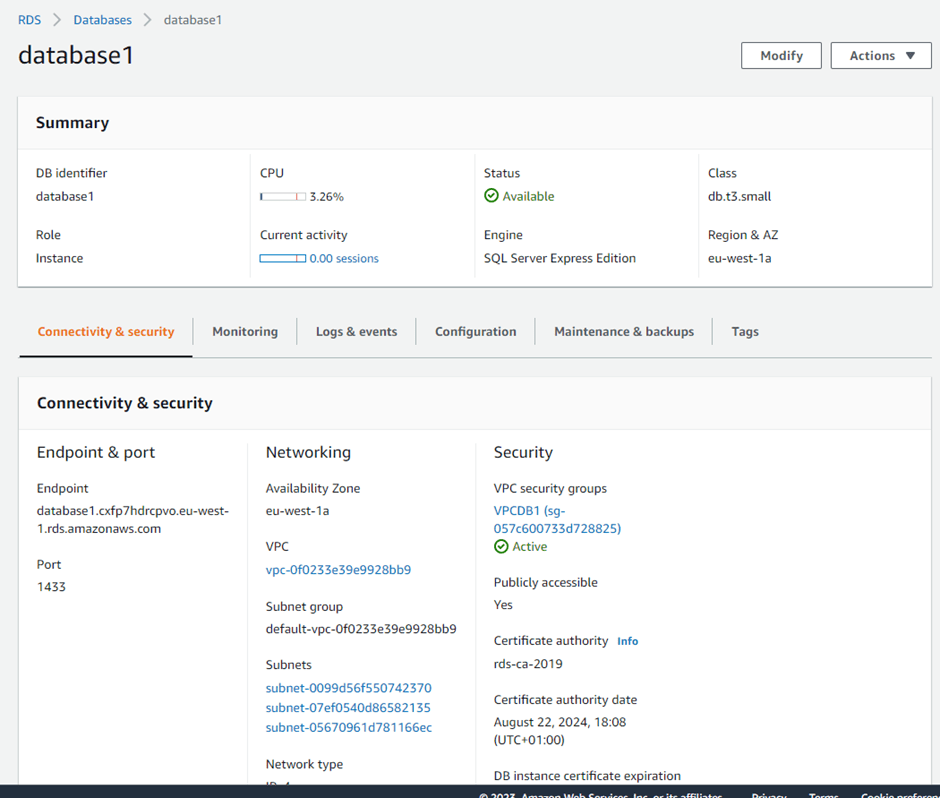
Once the instance is created, note down the Endpoint which serves as the connection string.
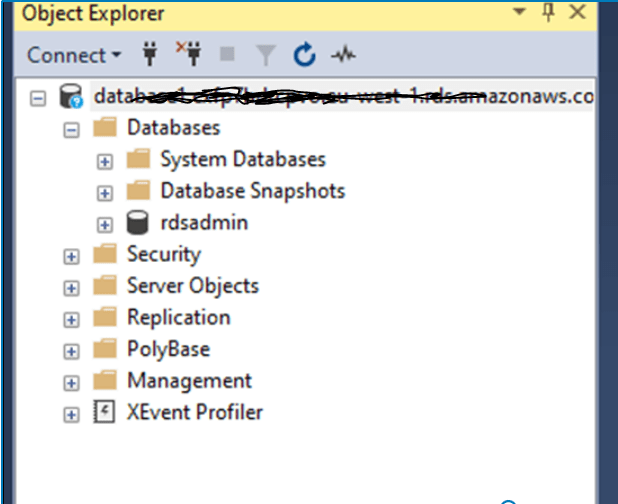
Use your preferred SQL Server client (e.g., SQL Server Management Studio) to connect to the instance using the provided credentials.
Initially got this
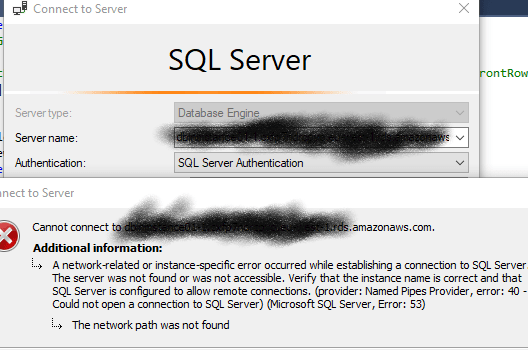
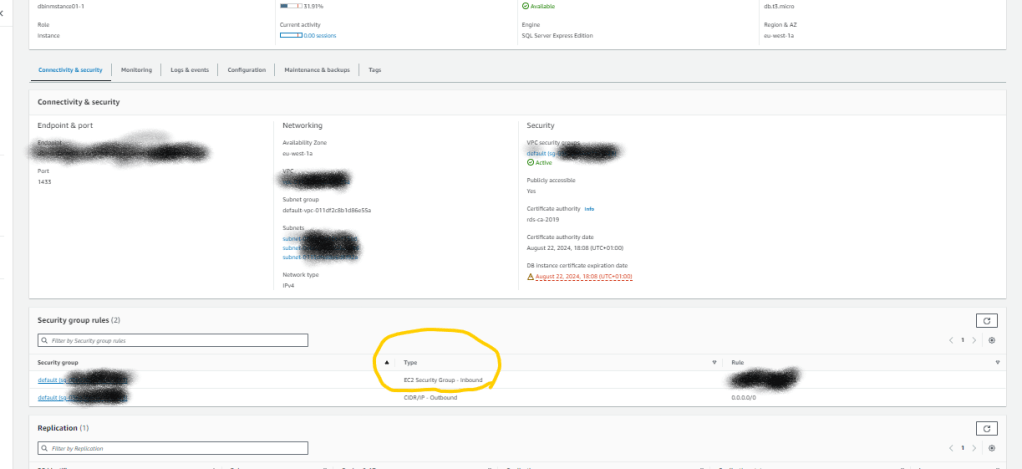
In the connectivity and Security
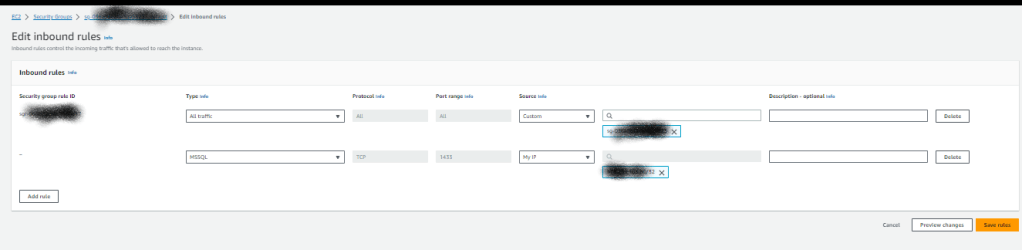
Click the Security group rules – Edit inbound rule and add
Type:MSSQL
Source My IP:
Type:MSSQL
Source My IP:choose your IP
Conclusion
That’s it! You’ve successfully set up a Microsoft SQL Server instance on Amazon RDS. Remember to secure your instance, configure backups, and monitor performance as per your requirements.
Remember to continuously monitor your resources and adjust configurations as your needs evolve. Happy data managing!